Pictorial supplement to The Fifth Kingdom - Chapter 11b
Fungal Ecology - part 2
A comparison of fungi in streams and ponds
(24 pictures)
[my grateful thanks to Prof. Felix Baerlocher and Dr. John Michaelides,
whose Ph.D. thesis work made this section of the chapter possible]
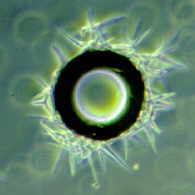
Amphibious fungi in streams - tetraradiate conidia in stream water trapped by a tiny air-bubble. This why foam is a good source of spores.

Amphibious fungi in streams - tetraradiate conidia of Lemonniera from stream water.
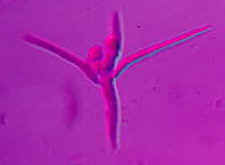
Amphibious fungi in streams - a tetraradiate conidium of Tetracladium from stream water

Amphibious fungi in streams - a tetraradiate conidium of Lemonniera from stream water

Amphibious fungi in streams - a tetraradiate conidium of Clavariopsis (SEM). Arrows indicate percurrent extensions of conidiogenous cell.
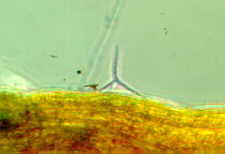
Amphibious fungi in streams - a tetraradiate conidium making a 3-point landing on a dead leaf.
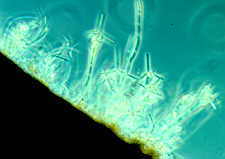
Amphibious fungi in streams - conidiophores and conidia of Lemonniera arising from a dead leaf

Amphibious fungi in streams - Gammarus, eater of leaves and fungi

Amphibious fungi in streams - feeding experiment showing Gammarus (dark dots) choosing fungal cultures (grey lines) over dead leaf material (dark circles)

Amphibious fungi in streams - feeding experiment showing how inoculation with specific fungi can reverse usual preference for leaf species.
Aero-aquatic fungi in ponds

Aero-aquatic fungi in ponds - the pond in Autumn

Aero-aquatic fungi in ponds - floating leaves which have just fallen into the pond.

Aero-aquatic fungi in ponds - the pond in winter

Aero-aquatic fungi in ponds - the pond in spring

Aero-aquatic fungi in ponds - conidiophores emerging from the water in summer, and developing into....
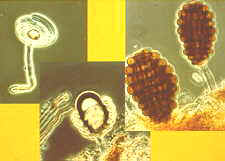
....coiled, hollow conidia of Helicoon

Aero-aquatic fungi in ponds - conidia of Helicoon arising from an inoculated leaf.

Aero-aquatic fungi in ponds - hollow, air-trapping conidia of Helicoon ellipticum (two containing bubbles).
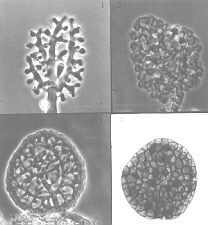
Aero-aquatic fungi in ponds - development stages of the hollow, floating propagules of Beverwykella

Aero-aquatic fungi in ponds - propagules of Beverwykella arising from an inoculated leaf
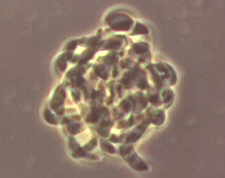
Aero-aquatic fungi in ponds - complex conidium of Spirosphaera, another genus with propagules that trap air.

Aero-aquatic fungi in ponds - tree-frog-spawn in the pond.

Aero-aquatic fungi in ponds - skeletonized leaf from the pond - leaf and fungi have been eaten by snails and tree-frog tadpoles.

Aero-aquatic fungi in ponds - tree frog - the top of the food pyramid in the pond
Go to Chapter 11c Go to Table of Contents
© Mycologue publications 2020
